The cloud market continues to grow rapidly, and in 2025, three providers dominate almost every industry conversation: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). While all three offer world class infrastructure and services, they each excel in different ways. Understanding their strengths helps you choose the right platform for your project, certification journey, or long term career path.
In this guide, you will learn why these three cloud vendors lead the market, what each one is best known for, and which workloads fit each cloud provider. We will also cover popular services, strengths, weaknesses, and how to choose based on your goals in cybersecurity, cloud engineering, DevOps, and AI.
Market Share Overview
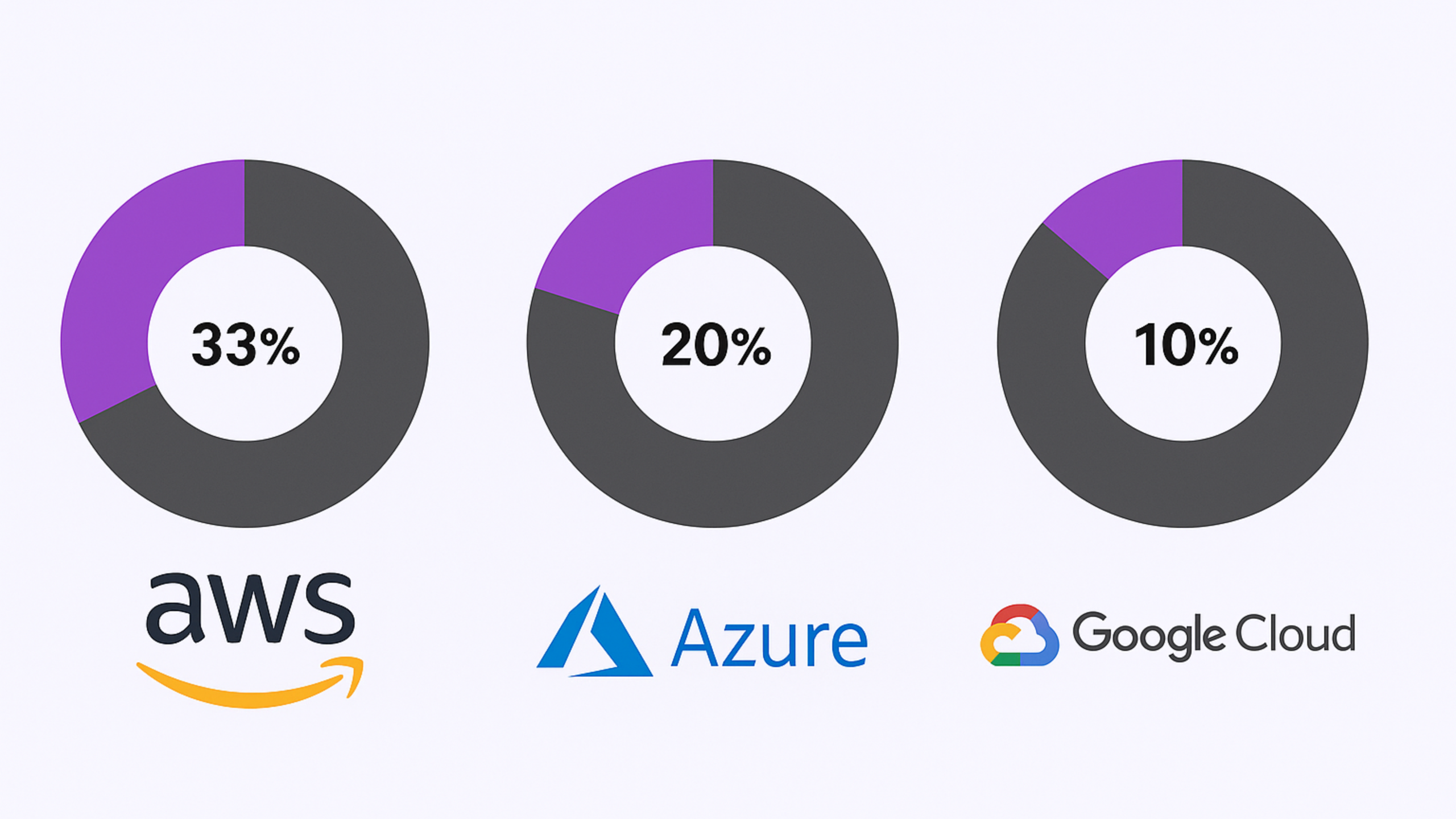
According to industry data, the top three cloud providers hold a significant share of the global cloud infrastructure market.
-
AWS: around 30 to 33 percent
-
Azure: around 20 to 25 percent
-
Google Cloud: around 10 to 13 percent
These numbers shift slightly each quarter, but the pattern remains consistent. AWS leads with the broadest adoption, Azure dominates in enterprise and hybrid environments, and Google Cloud leads in data, analytics, and AI driven workloads.
Why Those 3 Dominate the Market, and What About the Rest?
AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud dominate the market because they offer the widest global infrastructure, the most complete set of cloud services, and the strongest enterprise trust. Their ecosystems cover every major workload from compute to AI, and they invest heavily in compliance, security, and innovation.
Other providers like Oracle Cloud, IBM Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, and DigitalOcean serve more specialized or regional needs, but they lack the scale, maturity, and multi industry adoption that the top three have built over the past decade.
1. AWS (Amazon Web Services)
The most mature, widely adopted, and comprehensive cloud platform
Launched in 2006, AWS was the first large scale public cloud and remains the most feature rich platform today. It has the widest global footprint, the deepest service catalog, and the strongest ecosystem support. Developers, enterprises, startups, and governments rely on AWS for virtually every type of workload.
Explore: https://aws.amazon.com
Why AWS is #1
-
Longest time in the market with global reliability
-
Extremely large range of managed services
-
High scalability for fast growing applications
-
Strong community, documentation, and training support
-
Trusted by major enterprises, SaaS companies, and regulated industries
Best Use Cases
-
Cloud native startups and SaaS platforms
-
Scalable backend systems and microservices
-
Global applications needing multi region deployment
-
DevOps and automation heavy environments
-
Security focused workloads with strong IAM and network controls
Most Popular AWS Services
-
EC2: compute and virtual machines
https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/ -
S3: low cost, durable object storage
https://aws.amazon.com/s3/ -
Lambda: serverless compute for event based workloads
https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/ -
RDS: managed relational databases
https://aws.amazon.com/rds/ -
DynamoDB: fully managed NoSQL database
https://aws.amazon.com/dynamodb
AWS remains the most flexible and capable platform for diverse workloads, making it a strong choice for engineers, developers, and certification candidates who want a broad foundation. This one is my favourite CSP.
2. Microsoft Azure
The leading cloud for enterprises, hybrid environments, and Microsoft integrated workloads
Azure excels because it seamlessly integrates with the tools businesses already use. Organizations that rely on Windows Server, Active Directory, Office 365, or Microsoft 365 often choose Azure because it reduces complexity and improves governance.
Explore: https://azure.microsoft.com
Why Azure is #2
-
Deep integration with Microsoft enterprise ecosystem
-
Strong hybrid cloud capabilities and easy on prem extension
-
Preferred choice for organizations modernizing legacy infrastructure
-
Large enterprise adoption across industries
-
Advanced identity and governance tools
Best Use Cases
-
Enterprises using Windows, AD, Microsoft 365
-
Hybrid cloud deployments and on prem integration
-
Identity centric workloads and governance heavy environments
-
Regulated industries with strict compliance requirements
-
Migration of legacy workloads to cloud
Most Popular Azure Services
-
Azure Virtual Machines: compute and OS workloads
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/ -
Azure App Service: managed web hosting
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/ -
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): container orchestration
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/aks/ -
Azure SQL: managed relational database
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/ -
Azure Active Directory: identity, access, SSO, IAM
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/entra/identity/
Azure remains the strongest option for enterprise modernization, hybrid environments, and organizations already embedded in Microsoft’s ecosystem.
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
The leader in AI, data, analytics, and developer friendly cloud services
Google Cloud is known for its advanced analytics engines, AI and machine learning products, and world class container orchestration tools. Companies that need high performance data engineering pipelines, ML workloads, or large scale analytics often choose GCP.
Explore: https://cloud.google.com
Why GCP is #3
-
Best in class data and analytics solutions
-
Strong AI and machine learning ecosystem
-
Container and Kubernetes leadership (Google created Kubernetes)
-
Transparent pricing and developer friendly tools
-
Rapid growth among tech companies, AI startups, and research organizations
Best Use Cases
-
Data heavy platforms and analytics systems
-
AI, machine learning, and model training
-
High performance compute and distributed workloads
-
Container native applications using Kubernetes
-
Modern web apps and scalable microservices
Most Popular GCP Services
-
BigQuery: serverless enterprise data warehouse
https://cloud.google.com/bigquery -
Vertex AI: end to end AI and ML development platform
https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai -
GKE: leading Kubernetes orchestration service
https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine -
Cloud Storage: globally distributed object storage
https://cloud.google.com/storage -
Compute Engine: flexible VMs and compute
https://cloud.google.com/compute
GCP is ideal for teams building advanced analytics, AI driven tools, or highly scalable container based systems.
Which Cloud Is Better for What
Below is a simplified breakdown considering workload type, strategy, and engineering priorities.
| Use Case | Best Cloud Provider |
|---|---|
| Enterprise and Hybrid Cloud | Azure |
| Startups, SaaS, and Global Scaling | AWS |
| Data Engineering, AI, ML, and Analytics | Google Cloud |
| Kubernetes and Modern App Architecture | Google Cloud |
| Compliance Heavy Industries | Azure or AWS |
| Pricing Transparency | Google Cloud |
| Overall Service Breadth | AWS |
Multi Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Strategy
Most big companies use a multi cloud approach for flexibility, cost control, and vendor risk reduction. For example:
-
Use Azure for enterprise identity, governance, and Microsoft 365 integration
-
Use AWS for global app deployment and microservices
-
Use GCP for analytics and data engineering pipelines
This combination allows organizations to get the strongest features from each cloud.
Choosing the Cloud Provider for Your Career
Choose AWS if you want
-
Broad cloud knowledge
-
DevOps, automation, or cloud architecture roles
-
Work in startups or diverse technical environments
Choose Azure if you want
-
Enterprise IT, corporate IT, or cloud governance roles
-
Work with Microsoft technologies and identity systems
-
Security, compliance, or hybrid cloud positions
Choose GCP if you want
-
AI and ML engineering roles
-
Data engineering or analytics jobs
-
Work in tech companies and high growth AI startups
Certifications from all three providers are valuable, but AWS and Azure remain the most requested in job listings.